Share this page
Minimizing the need for antimicrobial use
To minimize the need for antimicrobial use, the dairy sector encourages good animal health and welfare
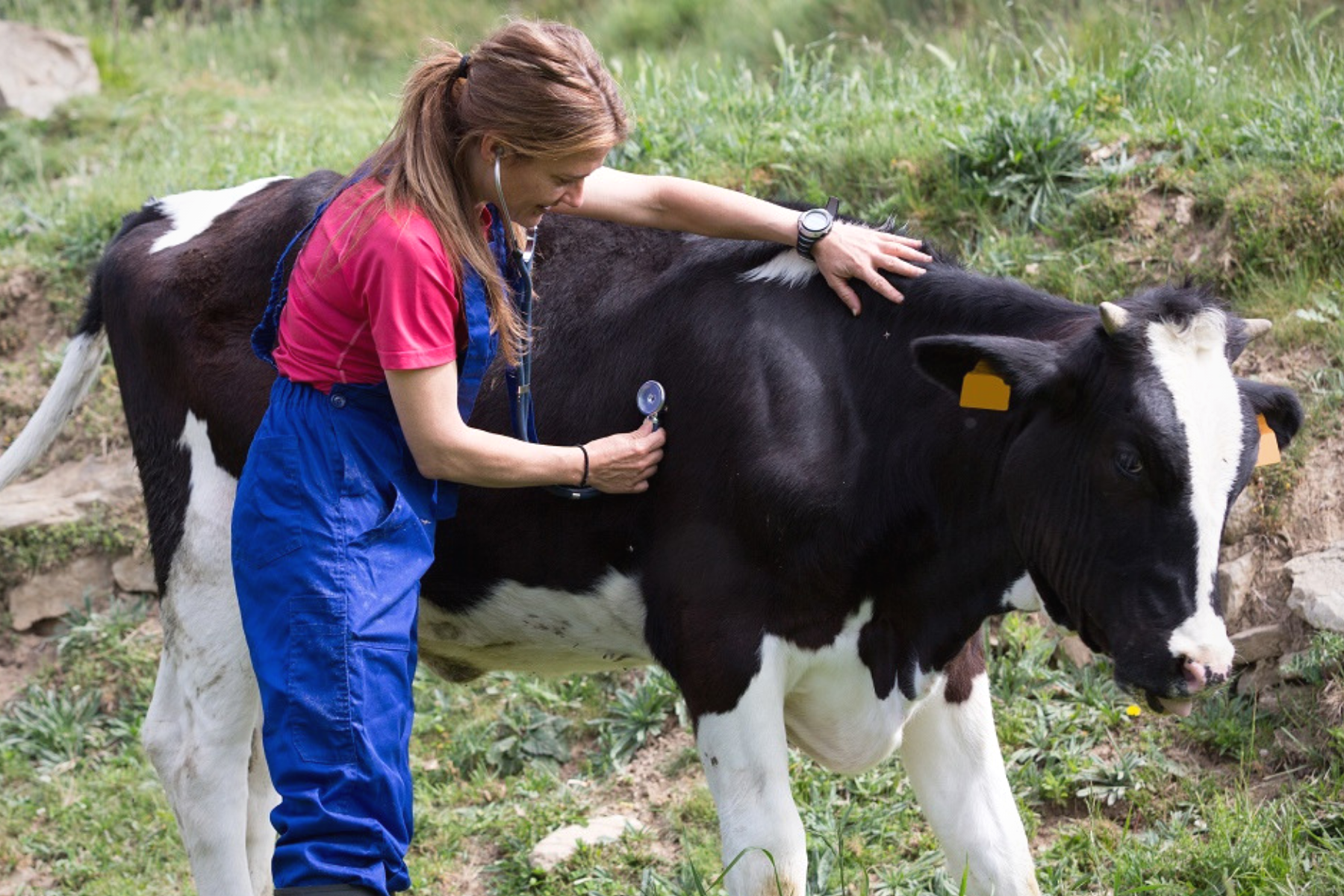

IDF promotes prudent and responsible use of antimicrobial agents within the global dairy sector to ensure that they continue to be effective and useful for curing diseases in animals.
Antimicrobials are medicines used to treat infections, particularly those caused by bacteria, to maintain human and animal health. Some bacteria have developed full or partial resistance to various antimicrobial agents. Resistance occurs naturally in bacteria through spontaneous mutation or natural selection but can be accelerated due to incorrect use of antibiotics in human medicine, animal medicine, and plant medicine. This phenomenon is known as antimicrobial resistance or AMR.
Addressing AMR is important, because it limits the range of antimicrobial agents that can be used to treat infections effectively.
The emergence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria has had profound effects on the management of therapeutic approaches to both human and veterinary diseases. It can mean an increase in the prevalence and severity of disease in humans and animals, and impacts animal welfare, human health, food safety and food security. It may result in additional costs associated with treating infections due to the requirement to use newer, higher cost or multiple antimicrobials.
Effective management of AMR is complex. It is not constrained by geographic or human/animal borders, and resistant bacteria arising either in humans, animals or the environment may spread from one to the other, and from one country to another.
Within the dairy sector, antimicrobials are used to treat certain infectious diseases (such as mastitis, lameness and pneumonia). In most countries regulation and commercial incentives strictly control the use of antimicrobials. Dairy animals are treated individually, and non-therapeutic measures are incorporated in disease control. When antimicrobial agents are used, they are mostly administered locally for specific purposes.
Limiting the development of AMR requires the implementation of global strategies by public health, veterinary and environmental authorities in all countries of the world. At a national level, with respect to animal health services, these include:
- Communication and awareness-raising of all stakeholders involved
- Adequate legislation on the prescription and use of antimicrobial agents in humans and animals
- Good governance of national human and animal health systems
- A well-trained veterinary profession regulated by law and supervised by proper regulatory authorities
- Effective compliance management supporting responsible and prudent use strategies
More detailed information on measures that may be taken to combat AMR, read IDF’s Guidance on Antimicrobial Resistance from the Dairy Sector

Global approaches to manage AMR
The Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance was developed in 2015 and underscores the need for an effective “One Health” approach involving coordination among numerous international sectors and actors, including human and veterinary medicine, agriculture, finance, environment, and well-informed consumers. Development of this plan was guided by the advice of countries and key stakeholders, based on several multi-stakeholder consultations at different global and regional forums.
Since 2019, IDF has been a partner of the DISARM project, a thematic network under the EU Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program.
DISARM focuses on disseminating innovative solutions in the livestock industry to reduce antibiotic use and consequently reduce and prevent antimicrobial resistance. The goal is to assist the livestock sector to shift towards a prudent use of antibiotics by focusing on better biosecurity and improved animal health and disease prevention and targeted and precise use of antibiotic treatments.
Learn more about animal health & welfare
The breadth of issues IDF covers in its work is extensive. Find out more about the work we do.
Promoting the welfare of dairy animals
For a dairy farmer to be successful at producing milk of good quality, the welfare needs of dairy animals must be met.....
Read MoreExcellent udder health for high quality milk
Excellent udder health during lactation results in high quality milk.
Read MoreCalf care from birth to weaning
The animal health and welfare management of calves from birth to weaning is of great importance to the dairy sector, as healthy calves lead to healthy....
Read MoreHeat stress in dairy cattle
Heat stress in dairy cows can have negative consequences for milk production, and for reproduction, welfare and health.....
Read MoreHeat stress in dairy cattle
Heat stress in dairy cows can have negative consequences for milk production, and for reproduction, welfare and health.....
Read MoreRelated reports & publications
IDF provides a permanent source of authoritative scientific and other information on a whole range of topics relevant to the dairy sector.
Bulletin of the IDF N° 498/2019: The IDF Guide to Good Animal Welfare in Dairy Production 2.0...
This guide provides recommendations on stockmanship, feed and water, physical environment, husbandry practices....
Guide to Good Dairy Farming Practice in English (2011)
This Guide gives individual dairy farmers proactive guidance on how these objectives can be achieved on their....
IDF Animal Health Report N° 14
The 14th edition of the IDF Animal Health Report illustrates the importance of animal health and welfare for s....
IDF Animal Health Report N° 13
IDF's 13th edition of the IDF Animal Health Report. This latest tool to share knowledge in dairy welfare was r....
Related news & insights
IDF provides a permanent source of authoritative scientific and other information on a whole range of topics relevant to the dairy sector.