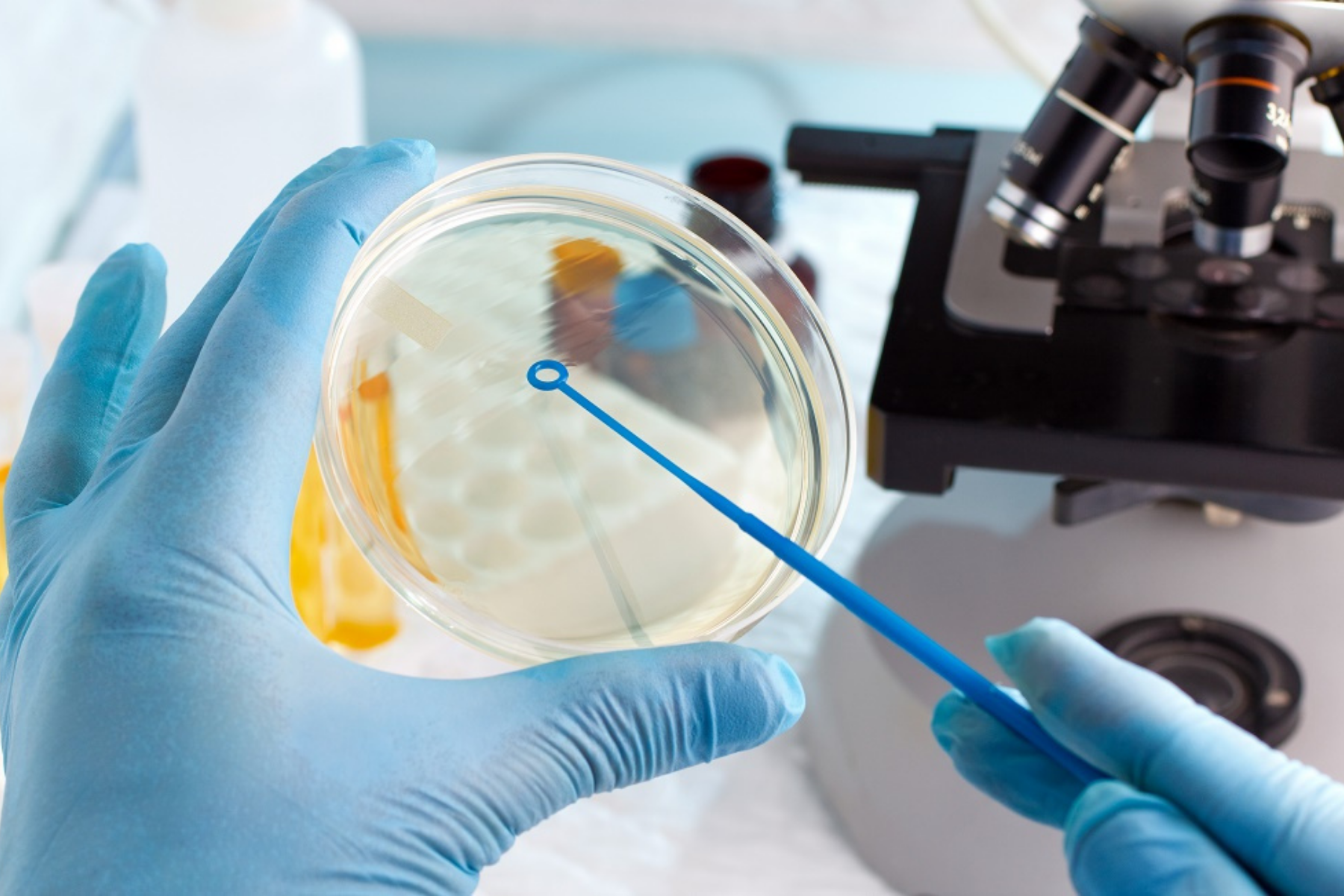
The aims of this update of the ISO/IDF guide on the conversion of bacteria units have been to improve on the statistical model and at the same time increase the user-friendliness, as levels of statistical knowledge between users vary considerably.
ISO 21187|IDF 196 is especially important to laboratories accredited according to ISO 17025, such as interprofessional laboratories analyzing raw milk for farmer settlement. However, also dairy plants make use of bacteria counters for instant testing of raw milk for regulatory purposes and self-monitoring programs. The major changes found in this version are:
- The formula describing the conversion relation has been based on aggregating individual results into groups, rather than data from individual sample measurements;
- Practical examples have been given in a spreadsheet on how to perform calculation and verification of conversion relationships including outliers test.
By giving clear examples on how to develop a conversion relationship and how to verify its statistical difference with an already existing one, the document will serve as a practical guide for stakeholders – from the smaller dairy laboratories to the highly specialized raw milk payment organizations and regulatory bodies. The document can help to make decisions on how to carry out the development and maintenance of conversion equations.
Even if simplified, the procedure for the building of a conversion relationship still requires a large number of samples to produce sufficient datasets(typically 600 + samples). The organizers may need to consider whether to perform the testing in a single lab or to team up with partners to cover larger geographical areas and to reduce the workload.
ISO 21187 | IDF 196 Milk – Quantitative determination of microbial quality – Guidance for establishing and verifying a conversion relationship between results of an alternative method and anchor method results is available to purchase here.